PCブラウザに接続したUSBゲームパッドを操作する。
ラズパイ側は python の websocket で待ち受け・受信する。
[ゲームパッド]ー[PCブラウザ]ー[Wi-Fi]ー[ラズパイ websocket]
その1.PCブラウザのHTML
ラズパイのwebディレクトリに 新しいファイル[controller.html]を作成する。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<title>Gamepad to Raztank</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<h2>Gamepad Input for Raztank Python</h2>
<p>
Gamepad: <span id="gamepad"></span><br>
WebSocket: <span id="websockets"></span>
</p>
<pre id="output"></pre>
<script>
let socket;
let lastData = null; // 前回送信したデータを保持
// WebSocketイベントが発生したら表示変更
const wsStatus = document.getElementById("websockets");
function connectWebSocket() {
socket = new WebSocket("ws://razpi43.local:8765/gamepad");
socket.onopen = () => wsStatus.textContent = "接続成功";
socket.onerror = () => wsStatus.textContent = "エラー";
socket.onclose = () => {
wsStatus.textContent = "切断";
setTimeout(connectWebSocket, 3000); // 3秒毎に接続トライ
}
}
function pollGamepad() {
const gp = navigator.getGamepads()[0];
if (gp) {
const data = {
buttons: gp.buttons.map(b => b.pressed),
axes: gp.axes
};
const jsonData = JSON.stringify(data);
document.getElementById("output").textContent = jsonData;
// データが変化している場合のみ送信
if (socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN && jsonData !== lastData) {
socket.send(jsonData);
lastData = jsonData;
}
}
requestAnimationFrame(pollGamepad);
}
window.addEventListener("gamepadconnected", () => {
document.getElementById("gamepad").textContent = "接続成功";
pollGamepad();
});
// 初回websocket接続
connectWebSocket();
</script>
</body>
</html>その2.ラズパイ側のpythonコード
ラズパイ側では websocket 待ち受けし、PCブラウザからのwebsocket送信を待つ新しいファイル[test_receive.py]を作成する。
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
# デッドゾーン(微小な揺れを無視)
DEADZONE = 0.2
def get_left_stick_direction(axes):
x = axes[0] if len(axes) > 0 else 0
y = axes[1] if len(axes) > 1 else 0
direction = []
if abs(x) > DEADZONE:
direction.append("← 左" if x < 0 else "→ 右")
if abs(y) > DEADZONE:
direction.append("↑ 上" if y < 0 else "↓ 下")
return direction if direction else ["ニュートラル"]
async def handler(websocket):
async for message in websocket:
try:
data = json.loads(message)
axes = data.get("axes", [])
direction = get_left_stick_direction(axes)
print(f"方向: {', '.join(direction)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ エラー: {e}")
async def main():
print("🎧 WebSocketサーバー起動中(ポート8765)...")
async with websockets.serve(handler, "0.0.0.0", 8765):
await asyncio.Future() # 永久待機
asyncio.run(main())その3.接続検査する
まずラズパイ側で websocket 待ち受け[$ python gamepad_receive.py]を実行する。
PCブラウザではUSBゲームパッドを接続したら、[http://razpi**.local/gamepad_websocket.html]にアクセスする。
USBゲームパッドの左スティックを操作すると:
PC側ブラウザの画面表示は
Gamepad Input for Node-RED
{“buttons”:[false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false],”axes”:[0.000015259021896696368,-0.000015259021896696368,0.000015259021896696368,-0.000015259021896696368]}
また DevTools のコンソールには下図 ” Gamepad Connected ” が表示される
ラズパイのターミナル表示は下記:
🎧 WebSocketサーバー起動中(ポート8765)...
方向: → 右
方向: ニュートラル
方向: → 右
方向: ニュートラル
方向: ← 左
方向: ニュートラル
方向: ニュートラル以上。そしてもっとゲームパッドのキーを有効にするには:
ラズパイ側 python コードをゲームパッド全ボタン有効化
ラズパイ側の新しいファイル[test_receive2.py]を作成する。
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
DEADZONE = 0.2
BUTTON_NAMES = {
0: "A", 1: "B", 2: "X", 3: "Y",
4: "LB", 5: "RB", 6: "LT", 7: "RT",
8: "バック", 9: "スタート", 10: "左スティック押し込み",
11: "右スティック押し込み", 12: "十字 ↑", 13: "十字 ↓",
14: "十字 ←", 15: "十字 →", 16: "ガイド"
}
def get_stick_direction(name, x, y):
direction = []
if abs(x) > DEADZONE:
direction.append(f"{name} ← 左" if x < 0 else f"{name} → 右")
if abs(y) > DEADZONE:
direction.append(f"{name} ↑ 上" if y < 0 else f"{name} ↓ 下")
return direction if direction else [f"{name} ニュートラル"]
def get_pressed_buttons(buttons):
return [
BUTTON_NAMES.get(i, f"ボタン{i}")
for i, pressed in enumerate(buttons)
if pressed
] or ["なし"]
async def handler(websocket):
async for message in websocket:
try:
data = json.loads(message)
axes = data.get("axes", [])
buttons = data.get("buttons", [])
# 左スティック(axes[0], axes[1])
lx = axes[0] if len(axes) > 0 else 0
ly = axes[1] if len(axes) > 1 else 0
left_direction = get_stick_direction("左スティック", lx, ly)
# 右スティック(axes[2], axes[3])
rx = axes[2] if len(axes) > 2 else 0
ry = axes[3] if len(axes) > 3 else 0
right_direction = get_stick_direction("右スティック", rx, ry)
pressed = get_pressed_buttons(buttons)
print(f"左スティック: {', '.join(left_direction)}")
print(f"右スティック: {', '.join(right_direction)}")
print(f"ボタン: {', '.join(pressed)}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"⚠️ エラー: {e}")
async def main():
print("🎮 WebSocketサーバー起動中(ポート8765)...")
async with websockets.serve(handler, "0.0.0.0", 8765):
await asyncio.Future()
asyncio.run(main())検査結果
🎮 WebSocketサーバー起動中(ポート8765)...
右スティック: 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ↑ 上
ボタン: B
ボタン: X
ボタン: RT
ボタン: LT, RT
ボタン: LT
ボタン: LB
ボタン: RB
右スティック: 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上
右スティック: 右スティック ← 左, 右スティック ↑ 上ラズタンクのモータードライバーと接続する[キーボードで操作]
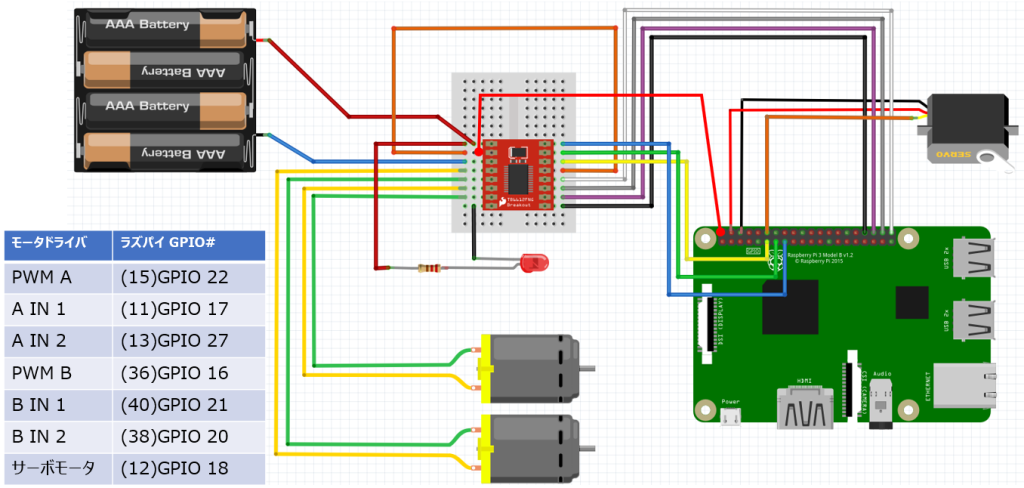
このコードは下図配線の場合です。自分のGPIO番号にあわせて変更してください。
Pythonでキー入力を検知する readchar モジュールをインストールします。
$ sudo pip install readcharラズタンクをキー操作するPythonコードは下記の通りです。
例えば[$ sudo nano tank.py]などで新しいファイルを作ってコードを書きます。
正しく入力できたら[$python tank.py]でプログラムを実行します。
操作は[w]キーで前進、[a]キーで左反転、[s]キーで右反転、[z]キーが後進です。
終了は[q]キー。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import sys
import time
import readchar
constLeftPWM = 17
constLeftIN1 = 27
constLeftIN2 = 22
constRightPWM = 16
constRightIN1 = 20
constRightIN2 = 21
GPIO.setwarnings( False )
GPIO.setmode( GPIO.BCM )
GPIO.setup( constLeftPWM, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constLeftIN1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constLeftIN2, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightPWM, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightIN1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightIN2, GPIO.OUT )
pwmLeft = GPIO.PWM( constLeftPWM, 50 ) #50Hz
pwmLeft.start( 0.0 )
pwmRight = GPIO.PWM( constRightPWM, 50 ) #50Hz
pwmRight.start( 0.0 )
def moveForward():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
def speedSlow():
pwmLeft.ChangeDutyCycle( 80 )
pwmRight.ChangeDutyCycle( 80 )
def speedHigh():
pwmLeft.ChangeDutyCycle( 100 )
pwmRight.ChangeDutyCycle( 100 )
def moveBack():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 1 )
def moveLeft():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
def moveRight():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 1 )
def moveStop():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
def end():
pwmLeft.stop()
pwmRight.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
sys.exit(0)
######################################
# メインルーチン
######################################
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
while True:
kb = readchar.readchar()
sys.stdout.write(kb)
if kb == 'w':
speedHigh()
moveForward()
if kb == 'z':
speedSlow()
moveBack()
if kb == 'a':
speedSlow()
moveLeft()
if kb == 's':
speedSlow()
moveRight()
if kb == 'x':
moveStop()
if kb == 'q':
end()
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
moveStop()
end()ラズタンクのモータードライバーと接続する[Gamepadで操作]
新しく nano で [raztank.py] を作って、コピペする
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import sys
import time
import asyncio
import websockets
import json
# ラズパイのGPIO番号は自分の配線と一致させること
constLeftPWM = 22
constLeftIN1 = 17
constLeftIN2 = 27
constRightPWM = 16
constRightIN1 = 21
constRightIN2 = 20
# GPIOの初期設定
GPIO.setwarnings( False )
GPIO.setmode( GPIO.BCM )
GPIO.setup( constLeftPWM, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constLeftIN1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constLeftIN2, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightPWM, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightIN1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( constRightIN2, GPIO.OUT )
# PWM初期設定
pwmLeft = GPIO.PWM( constLeftPWM, 50 ) #50Hz
pwmLeft.start( 0.0 )
pwmRight = GPIO.PWM( constRightPWM, 50 ) #50Hz
pwmRight.start( 0.0 )
# モーター前進
def moveForward():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
# モーター低速
def speedSlow():
pwmLeft.ChangeDutyCycle( 80 )
pwmRight.ChangeDutyCycle( 80 )
# モーター高速
def speedHigh():
pwmLeft.ChangeDutyCycle( 100 )
pwmRight.ChangeDutyCycle( 100 )
# モーターバック
def moveBack():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 1 )
# モーター左
def moveLeft():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
# モーター右
def moveRight():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 1 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 1 )
# モーター停止
def moveStop():
GPIO.output( constLeftIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constLeftIN2, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN1, 0 )
GPIO.output( constRightIN2, 0 )
# プログラム終了
def end():
pwmLeft.stop()
pwmRight.stop()
GPIO.cleanup()
sys.exit(0)
# デッドゾーン(微小な揺れを無視)
DEADZONE = 0.2
# ゲームパッドのレバー・ボタン検出
def get_left_stick_direction(axes):
x = axes[0] if len(axes) > 0 else 0 # axes[0]:左スティックのX軸(左向き-1.0~右向き+1.0)
y = axes[1] if len(axes) > 1 else 0 # axes[1]:左スティックのY軸(上向き-1.0~下向き+1.0)
direction = []
if abs(x) > DEADZONE:
direction.append("← 左" if x < 0 else "→ 右")
if abs(y) > DEADZONE:
direction.append("↑ 上" if y < 0 else "↓ 下")
return direction if direction else ["ニュートラル"]
# レバー取得とモーター駆動
async def handler(websocket):
async for message in websocket:
try:
# ブラウザからwebsocketメッセージを取得する
data = json.loads(message)
# axesはスティックの値:[0]左レバーX軸, [1]左レバーY軸, [2]右レバーX軸, [3]右レバーY軸
axes = data.get("axes", [])
# レバー値の取得
direction = get_left_stick_direction(axes)
# デバッグ(検出したレバー名を表示する)
print(f"direction='{direction}', direction[0]='{direction[0]}'" +
(f", direction[1]='{direction[1]}'" if len(direction) > 1 else "") )
# モーターを駆動する
if direction[0] == "ニュートラル":
moveStop()
if direction[0] == "↑ 上":
speedHigh()
moveForward()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Gamepad取得エラー:{e}")
# メイン & 永久待機
async def main():
print("🎧 WebSocketサーバー起動中(ポート8765)...")
async with websockets.serve(handler, "0.0.0.0", 8765):
await asyncio.Future() # 永久待機
# ここからmain()を呼び出してずっと待機する
asyncio.run( main() )
以上